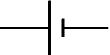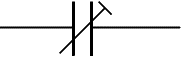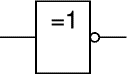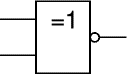Circuit symbols are used in circuit diagrams which show how a circuit is connected together. The actual layout of the components is usually quite different from the circuit diagram.
To build a circuit you need a different diagram showing the layout of the parts on stripboard or printed circuit board.
Temporary and trial circuits are often built on breadboardwhich does not require soldering.
Wires and connections
Component
Circuit Symbol
Function of Component
Wire

To pass current very easily from one part of a circuit to another.
Wires joined

A 'blob' should be drawn where wires are connected (joined), but it is sometimes omitted. Wires connected at 'crossroads' should be staggered slightly to form two T-junctions, as shown on the right.
Wires not joined

In complex diagrams it is often necessary to draw wires crossing even though they are not connected. The simple crossing on the left is correct but may be misread as a join where the 'blob' has been forgotten. The bridge symbol on the right leaves no doubt!
Power Supplies
Component
Circuit Symbol
Function of Component
Cell
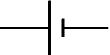
Supplies electrical energy.
The larger terminal (on the left) is positive (+).
A single cell is often called a battery, but strictly a battery is two or more cells joined together.
Battery

Supplies electrical energy. A battery is more than one cell.
The larger terminal (on the left) is positive (+).
Solar Cell

Converts light to electrical energy.
The larger terminal (on the left) is positive (+).
DC supply

Supplies electrical energy.
DC = Direct Current, always flowing in one direction.
AC supply

Supplies electrical energy.
AC = Alternating Current, continually changing direction.
Fuse

A safety device which will 'blow' (melt) if the current flowing through it exceeds a specified value.
Transformer

Two coils of wire linked by an iron core. Transformers are used to step up (increase) and step down (decrease) AC voltages. Energy is transferred between the coils by the magnetic field in the core. There is no electrical connection between the coils.
Earth
(Ground)
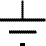
A connection to earth. For many electronic circuits this is the 0V (zero volts) of the power supply, but for mains electricity and some radio circuits it really means the earth. It is also known as ground.
Output Devices: Lamps, Heater, Motor, etc.
Component
Circuit Symbol
Function of Component
Lamp (lighting)

A transducer which converts electrical energy to light. This symbol is used for a lamp providing illumination, for example a car headlamp or torch bulb.
Lamp (indicator)

A transducer which converts electrical energy to light. This symbol is used for a lamp which is an indicator, for example a warning light on a car dashboard.
Heater
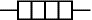
A transducer which converts electrical energy to heat.
Motor

A transducer which converts electrical energy to kinetic energy (motion).
Bell
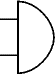
A transducer which converts electrical energy to sound.
Buzzer
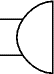
A transducer which converts electrical energy to sound.
Inductor
(Coil, Solenoid)

A coil of wire which creates a magnetic field when current passes through it. It may have an iron core inside the coil. It can be used as a transducer converting electrical energy to mechanical energy by pulling on something.
Switches
Component
Circuit Symbol
Function of Component
Push Switch
(push-to-make)

A push switch allows current to flow only when the button is pressed. This is the switch used to operate a doorbell.
Push-to-Break Switch

This type of push switch is normally closed (on), it is open (off) only when the button is pressed.
On-Off Switch
(SPST)

SPST = Single Pole, Single Throw.
An on-off switch allows current to flow only when it is in the closed (on) position.
2-way Switch
(SPDT)

SPDT = Single Pole, Double Throw.
A 2-way changeover switch directs the flow of current to one of two routes according to its position. Some SPDT switches have a central off position and are described as 'on-off-on'.
Dual On-Off Switch
(DPST)

DPST = Double Pole, Single Throw.
A dual on-off switch which is often used to switch mains electricity because it can isolate both the live and neutral connections.
Reversing Switch
(DPDT)

DPDT = Double Pole, Double Throw.
This switch can be wired up as a reversing switch for a motor. Some DPDT switches have a central off position.
Relay
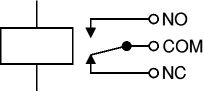
An electrically operated switch, for example a 9V battery circuit connected to the coil can switch a 230V AC mains circuit.
NO = Normally Open, COM = Common, NC = Normally Closed.
Resistors
Component
Circuit Symbol
Function of Component
Resistor

A resistor restricts the flow of current, for example to limit the current passing through an LED. A resistor is used with a capacitor in a timing circuit.
Some publications use the old resistor symbol: 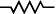
Variable Resistor
(Rheostat)

This type of variable resistor with 2 contacts (a rheostat) is usually used to control current. Examples include: adjusting lamp brightness, adjusting motor speed, and adjusting the rate of flow of charge into a capacitor in a timing circuit.
Variable Resistor
(Potentiometer)

This type of variable resistor with 3 contacts (a potentiometer) is usually used to control voltage. It can be used like this as a transducer converting position (angle of the control spindle) to an electrical signal.
Variable Resistor
(Preset)

This type of variable resistor (a preset) is operated with a small screwdriver or similar tool. It is designed to be set when the circuit is made and then left without further adjustment. Presets are cheaper than normal variable resistors so they are often used in projects to reduce the cost.
Capacitors
Component
Circuit Symbol
Function of Component
Capacitor

A capacitor stores electric charge. A capacitor is used with a resistor in a timing circuit. It can also be used as a filter, to block DC signals but pass AC signals.
Capacitor, polarised

A capacitor stores electric charge. This type must be connected the correct way round. A capacitor is used with a resistor in a timing circuit. It can also be used as a filter, to block DC signals but pass AC signals.
Variable Capacitor
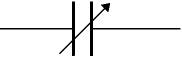
A variable capacitor is used in a radio tuner.
Trimmer Capacitor
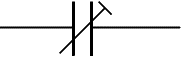
This type of variable capacitor (a trimmer) is operated with a small screwdriver or similar tool. It is designed to be set when the circuit is made and then left without further adjustment.
Diodes
Component
Circuit Symbol
Function of Component
Diode
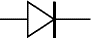
A device which only allows current to flow in one direction.
LED
Light Emitting Diode

A transducer which converts electrical energy to light.
Zener Diode
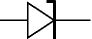
A special diode which is used to maintain a fixed voltage across its terminals.
Photodiode

A light-sensitive diode.
Transistors
Component
Circuit Symbol
Function of Component
Transistor NPN

A transistor amplifies current. It can be used with other components to make an amplifier or switching circuit.
Transistor PNP

A transistor amplifies current. It can be used with other components to make an amplifier or switching circuit.
Phototransistor

A light-sensitive transistor.
Audio and Radio Devices
Component
Circuit Symbol
Function of Component
Microphone

A transducer which converts sound to electrical energy.
Earphone

A transducer which converts electrical energy to sound.
Loudspeaker

A transducer which converts electrical energy to sound.
Piezo Transducer

A transducer which converts electrical energy to sound.
Amplifier
(general symbol)

An amplifier circuit with one input. Really it is a block diagram symbol because it represents a circuit rather than just one component.
Aerial
(Antenna)
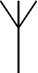
A device which is designed to receive or transmit radio signals. It is also known as an antenna.
Meters and Oscilloscope
Component
Circuit Symbol
Function of Component
Voltmeter

A voltmeter is used to measure voltage.
The proper name for voltage is 'potential difference', but most people prefer to say voltage!
Ammeter

An ammeter is used to measure current.
Galvanometer

A galvanometer is a very sensitive meter which is used to measure tiny currents, usually 1mA or less.
Ohmmeter

An ohmmeter is used to measure resistance. Most multimeters have an ohmmeter setting.
Oscilloscope

An oscilloscope is used to display the shape of electrical signals and it can be used to measure their voltage and time period.
Sensors (input devices)
Component
Circuit Symbol
Function of Component
LDR
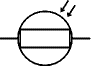
A transducer which converts brightness (light) to resistance (an electrical property).
LDR = Light Dependent Resistor
Thermistor

A transducer which converts temperature (heat) to resistance (an electrical property).
Logic Gates
Logic gates process signals which represent
true (1, high, +Vs, on) or
false (0, low, 0V, off).
For more information please see the
Logic Gates page.
There are two sets of symbols: traditional and IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission).
Gate Type
Traditional Symbol
IEC Symbol
Function of Gate
NOT
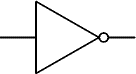
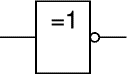
A NOT gate can only have one input. The 'o' on the output means 'not'. The output of a NOT gate is the inverse (opposite) of its input, so the output is true when the input is false. A NOT gate is also called an inverter.
AND
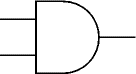
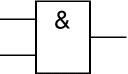
An AND gate can have two or more inputs. The output of an AND gate is true when all its inputs are true.
NAND

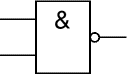
A NAND gate can have two or more inputs. The 'o' on the output means 'not' showing that it is a Not ANDgate. The output of a NAND gate is true unless all its inputs are true.
OR
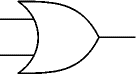
An OR gate can have two or more inputs. The output of an OR gate is true when at least one of its inputs is true.
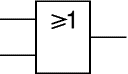
NOR
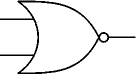
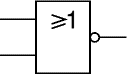
A NOR gate can have two or more inputs. The 'o' on the output means 'not' showing that it is a Not OR gate. The output of a NOR gate is true when none of its inputs are true.
EX-OR

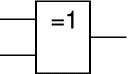
An EX-OR gate can only have two inputs. The output of an EX-OR gate is true when its inputs are different (one true, one false).
EX-NOR

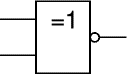
An EX-NOR gate can only have two inputs. The 'o' on the output means 'not' showing that it is a Not EX-ORgate. The output of an EX-NOR gate is true when its inputs are the same (both true or both false).
Sets of circuit symbols to download
You can download complete sets of all the circuit symbols shown above. The sets are 'zipped' for convenience and they are provided in three formats:
- WMF circuit symbols (32K) - Windows Metafiles.
These vector drawings are the best format for printed documents on most computer systems, including Windows where they can be used in Word documents for example. They can be enlarged without loss of quality. If you are not sure which format is best for you I suggest you try this one first. - GIF circuit symbols (43K) - Graphics Interchange Format.
These bitmap images are the best format for web pages but they print poorly and their bitmap nature will become obvious if they are enlarged. You can download individual symbols by saving the images used above on this page. - Drawfile circuit symbols (29K) - for RISC OS (Acorn) computers.
These high quality vector drawings are suitable for almost all documents on a RISC OS computer. All the symbols were originally drawn in this format. They print perfectly and can be enlarged without loss of quality. Sorry, this format is NOT suitable for Windows computers.
 Electricity is the flow of charge around a circuit carrying energy from the battery (or power supply) to components such as lamps and motors.
Electricity is the flow of charge around a circuit carrying energy from the battery (or power supply) to components such as lamps and motors.