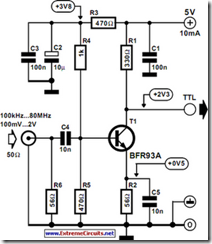
As the title implies, the present circuit is intended to convert sinusoidal input signals to TTL output signals. It can handle inputs of more than 100 mV and is suitable for use at frequencies up to about 80 MHz. Transistor T1, configured in a common-emitter circuit, is biased by voltage divider R3–R5 such that the potential across output resistor R1 is about half the supply voltage. When the circuit is driven by a signal whose amplitude is between 100 mV and TTL level (about 2 V r.m.s.), the circuit generates rectangular signals. The lowest frequencies that could be processed by the prototype were around 100 kHz at an input level of 100 mV, and about 10 kHz when the input signals were TTL level.Resistor R6 holds the input resistance at about 50 Ω, which is the normal value in measurement techniques. It ensures that the effects of long coaxial cables on the signal are negligible. If the converter is used in a circuit with ample limits, R6 may be omitted, whereupon the input resistance rises to 300 Ω.
http://www.extremecircuits.net/2010/06/sine-wave-to-ttl-converter.html
